Forklift Batteries: Lithium-Ion vs Lead-Acid
24 November 2022

Are you in the market for a forklift or a fleet of forklifts? If so, there are many factors to consider, such as capacity, application fit, vehicle dimensions, and lift height. But, perhaps, one of the most important decisions you'll have to make is whether to power the forklift with gas or electricity. If you choose an electric forklift, you'll then have to decide what battery technology will best suit your needs.
Like motor vehicles, electric forklifts are fast becoming the most popular lift trucks on the market. This is due to the fact that they are safer, cleaner and more reliable.
With recent changes to Australian Standards, electric forklifts must now have the speed reduced when the carriage is elevated to certain heights. Along with speed reduction on cornering, the risk of a rollover is greatly reduced making them safer than their LPG counterparts. The decision then is whether to use the traditional lead-acid battery or invest in lithium-ion batteries. Here's how the two options stack up in terms of the financial and operational aspects of running a forklift fleet.
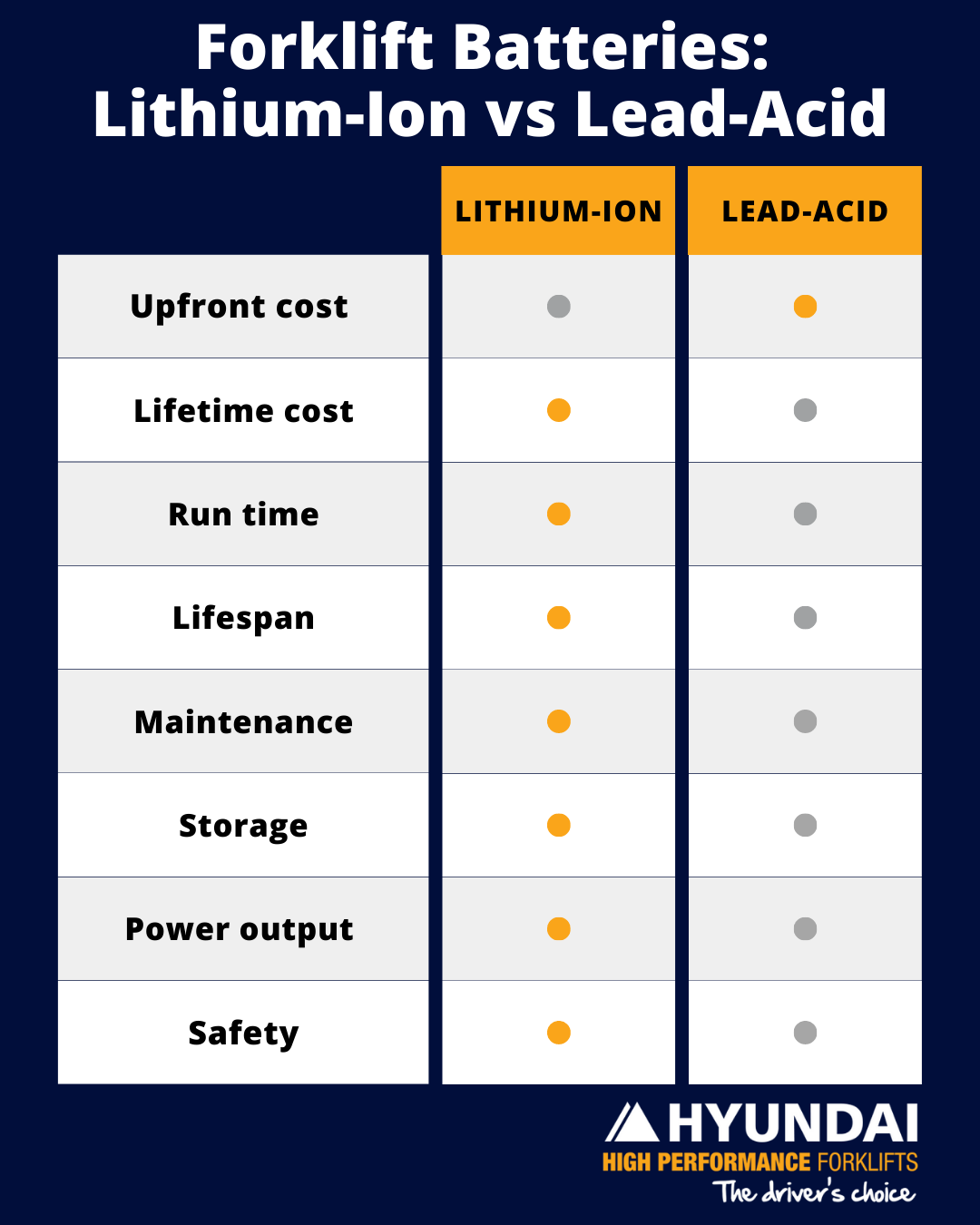
Upfront cost
A lithium-ion battery is more expensive than a lead-acid battery, however, as more lithium is manufactured to meet demand the cost is reducing. The higher price is also offset by the fact that the lithium battery will last 2-3 times the life of the lead acid battery.
Lifetime cost
Your operation will determine which option is the most productive and economical for your business. When looking at life time costs it’s important to remember that a lithium battery will last 2-3 times longer than a lead acid battery. This will depend on how well you maintain your lead acid battery. Lithium batteries require no maintenance so you will also need to assess the amount of labour required to maintain your lead acid battery. Your operation may also require additional lead acid batteries to achieve the required levels of productivity. The changing of batteries is also a costly and ineffective way to keep forklifts operational. In addition, lithium ion batteries and chargers are more energy efficient
Run time
The lead acid battery is a good option for operations that do not require multiple shifts because it can work for 8 hours with 16 hours of downtime (8 for charging and 4 hours for cooling down before and after the charging process). When you need more from your forklift, you should think about lithium. Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries are designed to be charged throughout the day (opportunity charged). This eliminates the need to swap batteries or wait for them to be fully charged.
Lifespan
You can expect a lithium-ion battery to last for 2,000 to 3,000 charge cycles. On the other hand, lead-acid batteries' lifespans are less predictable, as they depend on how well they are maintained. If they are not properly maintained or they are opportunity charged, cells will fail prematurely and have a shorter lifespan. Generally speaking, a well maintained lead acid battery will achieve 1,000 to 1,250 cycles.
Maintenance
In order to achieve maximum life, lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance. In some cases, distilled water is recommended and water levels need to be checked regularly. In addition, the terminals of each cell need to be checked and cleaned of corrosion. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are maintenance free and have a battery management system that records and displays all the critical data to ensure maximum life.
Storage
As lithium-ion batteries are stored and charged within the forklift. Depending on the size of the battery and charger, they can recharge the battery in 2-4 hours. They do not need to be swapped out during shifts. In many cases, the charger is built into the forklift. This reduces the storage area that would be needed for lead-acid batteries. They require dedicated charging areas and places to store the extra batteries for swapping if needed. You must also ensure that the charging area meets Australian Safety Standards for ventilation and safety measures such as acid spill kits and eyewash facilities.
Power output
The chargers for lithium ion batteries are more efficient than those for lead acid batteries. They deliver more power to the battery. In addition, as a lead acid battery discharges, the voltage drops, impacting the efficiency of major components such as the drive and lift motors. This can have an impact on their life cycles. In contrast, the lithium battery has no voltage drop, and the components can potentially have a longer, more efficient life cycle.
Safety
Charging and changing a lead-acid battery has an element of risk. Your staff must use specialised equipment and be fully trained to do the work. If improperly handled, incidents can occur. During the gassing stage, lead acid batteries emit gases. You should ensure your charging areas have sufficient ventilation and meet the required standards. Li-ion batteries, on the other hand, are sealed and do not need to be removed from the forklift to be charged, making them a much safer option.
Conclusion
This comparison makes it clear that lithium-ion is the better option overall. As a supplier, safety is key, but you should also think about your operating budget and needs.
If you need flexibility and are not ready to invest in a lithium option, or your needs may change as your business grows, Hyundai’s electric forklifts allow for easy conversion between lead acid and lithium-ion batteries!
No matter which battery you choose for your forklifts, there is little doubt electric forklifts are cleaner, cheaper to run, safer, and far more reliable than those driven by internal combustion engines.
Hyundai Forklifts Australian Forklift Champion crowned
Forklifts are a significant investment and purchasing one or hiring one via a lease can have huge consequences for your business. So what’s the best option? We’ve broken down the benefits and disadvantages of both options so you can make an informed decision, no matter which company you decide to purchase from.


